TASK MANAGER: A PREFERRED TOOL FOR POWER USERS
Introduction
Task manager a popular tool found as a default app in Windows. On a first glance of the task manager we can observe 7 major tabs(This blog focuses on w Microsoft has dramatically improved the Task Manager since the release of Windows 7.). Processes, Performance, App History, Startup apps, Users, Details, Services. The Task Manager is a fundamental utility tool in operating systems, providing a quick and accessible way to view and manage running processes, monitor system performance, and troubleshoot issues.
Different Tabs in Task manager
- Processes
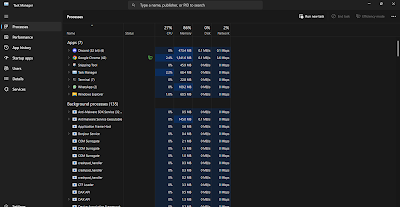
This tab basically displays all the processes running in the system at the moment, these include background processes, applications your running and sub processes ran by your applications. Not only does this tab mention which processes are being run but also mentions the CPU usage, Memory used, Disk Usage and Network used by each process. This tab is very helpful in understanding what exactly is happening in your pc and can also be used to close apps that aren't responding.
Other Options:
- Switch To: Switch to the application's window, bringing it to the front of your desktop and putting it in focus. This is useful if you're not sure which window is associated with which application.
- End Task: End the process. This works the same as the "End Task" button.
- Run New Task: Open the Create New Task window, where you can specify a program, folder, document, or website address and Windows will open it.
- Always On Top: Make the Task Manager window itself "always on top" of other windows on your desktop, letting you see it at all times.
- Open File Location: Open a File Explorer window showing the location of the program's .exe file.
- Search Online: Perform a Bing search for the program's application name and file name. This will help you see exactly what the program is and what it does.
- Properties: Open the Properties window for the program's .exe file. Here you can tweak compatibility options and see the program's version number, for example.
Commonly found 10 processes are
1) System Idle Process: This process doesn't consume any resources itself. It represents the percentage of CPU capacity not currently in use by other processes.
2) System: This process manages various system functions and services. It's a core part of the Windows operating system.
3) Desktop Window Manager (dwm.exe): This process is responsible for visual effects and rendering the desktop, including features like Aero Glass transparency.
4) Windows Explorer (explorer.exe): This process manages the Windows user interface, including the taskbar, desktop, and file management.
5) Taskmgr.exe: The Task Manager itself is also a process. It allows you to monitor and manage running processes, system performance, and other aspects of your system.
6) Microsoft Edge (msedge.exe): If you're using Microsoft Edge as your web browser, you might see its process here. Each open tab and extension runs within its own process.
7) Cortana (SearchUI.exe): Cortana is Microsoft's virtual assistant. The SearchUI.exe process manages the search functionality and Cortana's features.
8) Windows Security (SecurityHealthSystray.exe): This process is related to Windows Security, which provides antivirus, firewall, and other security features.
9) Microsoft OneDrive (OneDrive.exe): If you're using Microsoft OneDrive for cloud storage, its process manages the synchronization of files between your computer and the cloud.
10) Antivirus or Security Software: Depending on the antivirus or security software you have installed, you might see a process related to it. Common examples include "avastui.exe" for Avast, "mbamtray.exe" for Malwarebytes, etc.
This tab basically displays all the processes running in the system at the moment, these include background processes, applications your running and sub processes ran by your applications. Not only does this tab mention which processes are being run but also mentions the CPU usage, Memory used, Disk Usage and Network used by each process. This tab is very helpful in understanding what exactly is happening in your pc and can also be used to close apps that aren't responding.
Other Options:
Commonly found 10 processes are
This tab mainly focuses on all the system resources and provides graphs for monitor and data. This include read,write speeds, ram utilized, wifi used and more. Real-time graphs showing total CPU, memory, disk, network, and GPU resource usage for your system. You'll find many other details here, too, from your computer's IP address to the model names of your computer's CPU and GPU.
3) App History:
4) Startup-Apps
This page is my favourite as sometimes when we download new apps, they tend to automatically enable themselves to startup on every windows launch. While this can be helpful in some cases this can be annoying and as well as slow down the boot process and take a lot of computers resources which might not be needed at all times!. This tab lists all the apps that have been enabled for startup, or have had in the past (Shows disabled if so) and also mentions if there is a major impact on the pc during boot process. You can disable startup programs from here, although you can also do that from Settings > Apps > Startup.
Note: One additional thing you can also see in this tab is "BIOS time" which in my case is 3.9 seconds as mentioned my in screenshot below. This can help you understand how much time your computer took to start and if any apps are causing slower boots. (Windows 10 onwards only)
5) Users
This tab mentions the current logged in users in the pc and additionally also mentions the resources taken by the users at the moment for analysis or if you want to log out from certain accounts.
User processes, as seen in a task manager, refer to the programs and tasks that are initiated and controlled by the currently logged-in user. These processes are applications or software that the user launches and interacts with directly. They encompass tasks such as web browsers, office applications, media players, and other software that are part of the user's active work or entertainment. Monitoring user processes in a task manager allows users to assess which applications are running, their resource consumption, and the overall impact they have on system performance.
6) Details
This page can be slightly confusing as this page includes more detailed information about the processes running on your system. This is basically the traditional "Processes" tab from the Task Manager on Windows 7.
7) Services
The Services tab shows a list of the system services on your Windows system. These are background tasks that Windows runs, even when no user account is signed in. They're controlled by the Windows operating system. Depending on the service, it may be automatically started at boot or only when necessary. For example, the Windows Update service downloads updates and the Windows Audio service is responsible for sound. Other services are installed by third-party programs. For example, NVIDIA installs several services as part of its graphics drivers.
Difference between Processes and Services
In simple words, A process is a program which is started by the system (OS) or a third-party application. It is terminated once its purpose is done.
A service is a program which runs in the background, and does not terminate unless it encounters a problem, (example: an error).
A process is an instance of an executable file. That’s why there is at least one process running every time you open an app. A service, on the other hand, runs as an instance of the svchost.exe process, mostly (DLL files). That is the Windows service host process. Notice how svchost is also an executable file and the service host is itself a process? Again, a service can be a process, but a process may or may not be a service.
Clock. The clock is always running on your computer, whether you have it open or not. It is also running when your computer is in sleep or hibernate mode. Hell, it always gets the correct date and time even when you shut down your computer for hours.That is because it is a process with a service (W32Time) that runs in the background without needing a user to tell it what to do. However, you may edit it to your liking if you want using a user interface from Settings which is a process.
Conclusion
Task manager is a powerful tool found in most operating systems. This tool explains all processes and tasks and services which are being run in the computer. This helps to analyze and optimize a system for power users. While task manager can look difficult to learn in the beginning, as we use it, it can prove itself easy to use and very helpful. Thank you for spending time reading my blog
Resources
https://www.howtogeek.com/t-mobiles-new-go5g-plan-gets-you-yearly-phone-upgrades/
https://leetcode.com/discuss/interview-question/operating-system/125025/what-is-the-difference-between-process-and-service#:~:text=A%20process%20is%20a%20program,(example%3A%20an%20error).
https://www.guidingtech.com/difference-process-service-windows/#:~:text=A%20process%20is%20an%20instance%20of%20an%20executable%20file.,%2C%20mostly%20(DLL%20files).









Comments
Post a Comment